Publications and Media
Find out more about SuperNEMO and NEMO-3! Use the links on the right to browse an archive of talks and posters presented at conferences around the world, check out our journal articles, read our PhD students' theses, or see what the news media has to say about SuperNEMO.
Conference talks
NEMO collaborators present at conferences around the world. Catch up on our progress with this archive of slides.
SuperNEMO: double-beta decay searches with a tracker-calorimeter experiment
presented by Yves Lemière at The search for neutrinoless double-β decay: experimental and theoretical challenges, Trento, Italy, 3 February 2026
The SuperNEMO Double-Beta-Decay Experiment
presented by Emmanuel Chauveau at 24th International Workshop on Next Generation Nucleon Decay and Neutrino Detectors (NNN25), Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, 2 October 2025
Status of the SuperNEMO Experiment and physics objectives
presented by Maros Petro at NeuTel 2025, Padova, Italy, 30 September 2025
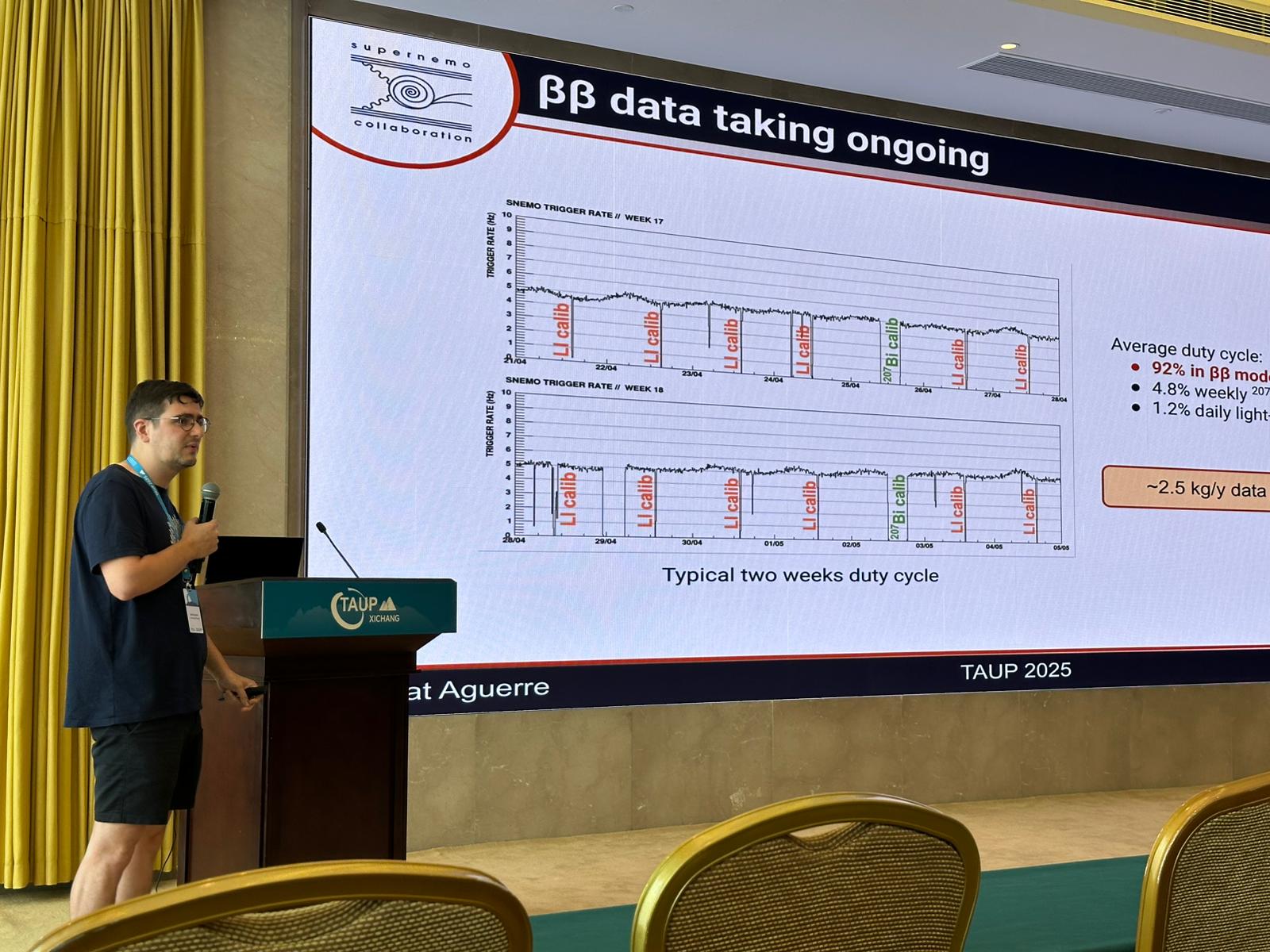
Status of the SuperNEMO Demonstrator and First Physics Data
presented by Xalbat Aguerre at TAUP 2025, Xichang, China, 25 August 2025
The SuperNEMO Double-Beta-Decay Experiment
presented by Cheryl Patrick at 21st Rencontres du Vietnam, Quy Nhon, Vietnam, 21 July 2025
Current Status of the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Sam Pratt at XIV International Conference on New Frontiers in Physics, Kolymbari, Crete, Greece, 18 July 2025
The SuperNEMO Demonstrator: a unique technology for high-precision measurements of $\beta\beta$-decay modes
presented by Miroslav Macko at EPS-HEP 2025, Marseille, France, 9 July 2025
Proceedings
Status of the SuperNEMO Experiment and sensitivity estimates to $0\nu\beta\beta$ and beyond
presented by Maros Petro at MEDEX 2025, Prague, Czech Republic, 27 June 2025
Proceedings
SuperNEMO demonsrator: status and objectives
presented by Christine Marquet at IRN Neutrino meeting, Lyon, France, 12 June 2025
Status update on the SuperNEMO double-beta-decay experiment
presented by William Quinn at WIN 2025, Brighton, UK, 10 June 2025
Neutron Backgrounds in the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Sam Pratt at IOP Joint APP and HEPP Annual Conference 2025, Cambridge, UK, 8 April 2025
Status of the SuperNEMO Demonstrator and Analysis of First Data
presented by Xalbat Aguerre at ICHEP 2024, Prague, Czech Republic, 19 July 2024
Proceedings
Status of SuperNEMO and Analysis of First Data
presented by Cheryl Patrick at TAUP 2023, Vienna, Austria, 30 August 2023
Proceedings
Commissioning of the SuperNEMO Demonstrator
presented by Malak Hoballah at 18th Recontres Du Vietnam, Quy Nhon, Vietnam, 21 July 2022
SuperNEMO Demonstrator Status
presented by Cheryl Patrick at IRN Neutrino meeting, Annecy, France, 30 June 2022
Search for Exotic Modes of Double Beta Decay within the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Maros Petro at MEDEX 2022, Prague, Czech Republic, 16 June 2022
Proceedings
Status of the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Alessandro Minotti at Conference on Neutrino and Nuclear Physics 2020, Cape Town, South Africa, 24 February 2020
Status of the SuperNEMO experiment
presented by Alessandro Minotti at 19th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Particle Physics, Moscow, Russia, 23 August 2019
Proceedings
Investigation of Mo-100 two-neutrino double beta decay in NEMO-3
presented by Victor Tretyak at MEDEX 2019, Prague, Czech Republic, 29 May 2019
Proceedings
The SuperNEMO Demonstrator double beta experiment
presented by Andrea Jeremie at VCI 2019, Vienna, Austria, 21 February 2019
Proceedings
The SuperNEMO project and final results from NEMO-3
presented by Cheryl Patrick at DBD-18, Hawaii, USA, 21 October 2018
Topological search for Matter Creation with NEMO-3 and SuperNEMO
presented by Ruben Saakyan at ICHEP 2018, Seoul, South Korea, 4 July 2018
Status of the SuperNEMO double-beta decay experiment
presented by Cheryl Patrick at IoP APP/HEPP Conference 2018, Bristol, UK, 27 March 2018
Radon Background Mitigation Strategy for the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Fang Xie at IoP APP/HEPP Conference 2018, Bristol, UK, 27 March 2018
Sensitivity Studies and Development of the Gas Supply System for the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Lauren Dawson at IoP APP/HEPP Conference 2018, Bristol, UK, 27 March 2018
Latest results from NEMO-3 and commissioning status of the SuperNEMO demonstrator
presented by Thibaud Le Noblet at TAUP2017, Sudbury, Canada, 28 July 2017
Proceedings
Radon emanation studies in the SuperNEMO double beta decay experiment
presented by Christophe Hugon at Rencontres du Vietnam 2017, Quy Nhon, Vietnam, 16 July 2017
Search for neutrinoless double-beta decay with the SuperNEMO demonstrator
presented by Carla Macolino at EPS-HEP2017, Venice, Italy, 7 July 2017
Proceedings
The NEMO-3 and SuperNEMO experiments
presented by Michele Cascella at TIPP 2017, Beijing, China, 22 May 2017
$0\nu\beta\beta$ sensitivity with the SuperNEMO demonstrator
presented by Steven Calvez at 52nd Rencontres de Moriond, YSF, La Thuile, Italy, 18 March 2017
Recent results from NEMO-3 and status of SuperNEMO
presented by Cristovao Vilela at DBD16, Osaka, Japan, 8 November 2016
Search for neutrinoless double-beta decay and measurement of double beta decay with two neutrinos with the NEMO-3 detector
presented by John Cesar at ICHEP 2016, Chicago, USA, 5 August 2016
Proceedings
Status of SuperNEMO Demonstrator
presented by Frédéric Perrot at ICHEP 2016, Chicago, USA, 5 August 2016
Proceedings
Latest results from NEMO-3 and status of the SuperNEMO Neutrinoless Double-Beta Decay experiment
presented by David Waters at Neutrino 2016, London, UK, 8 July 2016
Proceedings
Construction and commissioning of the tracker module for the SuperNEMO experiment
presented by Michele Cascella & Ashwin Chopra & Lauren Dawson at Neutrino 2016, London, UK, 4 July 2016
Proceedings
Radio-purity Strategy for the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Xin Ran Liu at IoP HEPP and AP joint meeting, Surrey, UK, 21 March 2016
Investigating $\beta\beta$ decay with NEMO-3 and SuperNEMO
presented by Summer Blot at TAUP 2015, Torino, Italy, 7 September 2015
Proceedings
SuperNEMO Physics with and without Neutrinos
presented by Karol Lang at NSAC NLDBD sub-panel, Washington DC, USA, 18 August 2015
Topological detection of $\beta\beta$-decay with NEMO-3 and SuperNEMO
presented by Ruben Saakyan at NDM-2015, Jyvaskyla, Finland, 4 June 2015
Construction and commissioning of the SuperNEMO detector tracker
presented by Michele Cascella at Frontier Detectors for Frontier Physics: 13th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors, Pisa, Italy, 27 May 2015
Proceedings
Radon emanation based material measurement and selection for the SuperNEMO double beta experiment
presented by Cedric Cerna at LRT2015, Seattle, Washington, USA, 19 March 2015
Proceedings
Ultra-low Level Radon Assays in Gases
presented by Xin Ran Liu at LRT2015, Seattle, Washington, USA, 18 March 2015
Proceedings
Latest results from NEMO-3 and status of SuperNEMO
presented by Alberto Remoto at NeuTel2015, Venice, Italy, 2 March 2015
Proceedings
The SuperNEMO experiment
presented by Federico Nova at WINP 2015, Brookhaven, USA, 5 February 2015
Search for Neutrinoless Double-$\beta$ Decay of $^{100}$Mo in the final NEMO-3 dataset
presented by Stefano Torre at XLIXth Rencontres de Moriond, La Thuile, Italy, 15 March 2014
Proceedings
Construction of the tracker for the SuperNEMO experiment
presented by Pawel Guzowski at NuPhys2013, London, UK, 19 December 2013
Proceedings
Results of the double beta decay experiment NEMO-3
presented by Victor Tretyak at MEDEX 2013, Prague, Czech Republic, 11 June 2013
Proceedings
Posters
SuperNEMO and NEMO-3 posters presented at conferences and schools.
He recycling system for SuperNEMO 0νββ detector
presented by Penghui Elvis Li at TAUP 2025, 27 August 2025
Reconstruction of Complex Particle Trajectories in the SuperNEMO Detector
presented by Tomas Krizak at EPS-HEP 2025, 9 July 2025
Proceedings
Study of Radon background in the SuperNEMO detector
presented by Antoine Lahaie / Xalbat Aguerre at ICHEP 2024, 18 July 2024
Proceedings
Searching for exotic modes of 2$\nu\beta\beta$ with the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Maros Petro at ICHEP 2024, 18 July 2024
Proceedings
Particle track reconstruction for the SuperNEMO experiment
presented by Tomas Krizak at ICHEP 2024, 18 July 2024
Proceedings
Measurement of the $\gamma$ background in Modane Underground Laboratory with SuperNEMO and estimation of SuperNEMO’s overall background
presented by Xalbat Aguerre/ Maros Petro/ Cheryl Patrick/ Christine Marquet/ Emmanuel Chauveau at XXXI International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics 2024, 18 June 2024
The SuperNEMO Demonstrator: a unique technology for high-precision measurements of $\beta\beta$-decay modes
presented by Miroslav Macko at XXXI International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics 2024, 18 June 2024
Proceedings
Development of software for energy calibration of the SuperNEMO Detector
presented by Filip Koňařík at XXXI International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics 2024, 18 June 2024
Proceedings
Radon contamination measurement in the SuperNEMO demonstrator
presented by Yegor Vereshchaka / Mathis Granjon / Laurent Simard at TAUP2023, 30 August 2023
Proceedings
First Energy Calibration of SuperNEMO’s Calorimeter using its Tracko-Calo Technology
presented by Filip Koňařík/ Tomáš Křižák/ Xalbat Aguerre at TAUP 2023, 30 August 2023
Proceedings
Commissioning of the SuperNEMO Demonstrator: A Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay Experiment
presented by Malak Hoballah/ Xalbat Aguerre/ William Quinn at Neutrino 2022, 30 May 2022
SuperNEMO calorimeter commissioning
presented by Cloe Girard-Carillo, Axel Pin, Christine Marquet, Mathieu Bongrand, Emmanuel Chauveau, Ramon Salazar, William Quinn, Hichem Tedjditi and Yves Lemiere at Neutrino 2020, 22 June 2020
SuperNEMO double-beta decay detector progress
presented by Cheryl Patrick at Neutrino 2020, 22 June 2020
SuperNEMO $0\nu\beta\beta$ sensitivity studies
presented by Lauren Dawson, Alessandro Minotti, Cheryl Patrick and Steven Calvez at Neutrino 2018, 4 June 2018
Study of Deposition Quality of $^{207}$Bi Calibration Sources for SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Miroslav Macko at Neutrino 2018, 4 June 2018
Radon Background Mitigation for the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Fang Xie and Christophe Hugon at Neutrino 2018, 4 June 2018
Latest Results of NEMO-3: $^{100}$Mo $2\nu\beta\beta$ decay measurement and search for Majoron and exotic processes
presented by Laurent Simard and Victor Tretyak at Neutrino 2018, 4 June 2018
Energy reconstruction with the SuperNEMO calorimeter
presented by Axel Pin, Christine Marquet and Emmanuel Chauveau at Neutrino 2018, 4 June 2018
Calibration Systems for the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Ramon Salazar, Karol Lang and Marek Proga at Neutrino 2018, 4 June 2018
Status of the SuperNEMO 0$\nu\beta\beta$ experiment
presented by Cheryl Patrick and Fang Xie at NuPhys2016, 12 December 2016
Proceedings
The SuperNEMO calorimeter
presented by Christine Marquet at ICHEP 2016, 5 August 2016
Proceedings
Searching for Periodic Variations in Nuclear Decay Rates using the NEMO-3 Detector
presented by John Cesar at ICHEP 2016, 5 August 2016
Proceedings
Radioactive source deployment system for the calibration of the SuperNEMO detector
presented by Ramon Salazar and Joshua Bryant at ICHEP 2016, 5 August 2016
Proceedings
Double-$\beta$ decay of $^{48}$Ca in NEMO-3
presented by Cristovao Vilela at ICHEP 2016, 5 August 2016
Measurement of the two-neutrino $\beta\beta$ decay half-life and a search for neutrinoless $\beta\beta$ decay of $^{82}$Se with NEMO-3
presented by James Mott at ICHEP 2016, 5 August 2016
The SuperNEMO $\beta\beta$ source production
presented by Andrea Jeremie and Alberto Remoto at ICHEP 2016, 5 August 2016
Proceedings
Gamma-tracking and sensitivity to gamma-emitting backgrounds in SuperNEMO
presented by Steven Calvez at ICHEP 2016, 5 August 2016
Proceedings
Status of the SuperNEMO Integration at LSM
presented by Mathieu Bongrand at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
Radon Mitigation Strategy and Results for the SuperNEMO Experiment
presented by Xin Ran Liu at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
Proceedings
Measurement of the 2$\nu\beta\beta$ decay half-life and search for the 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decay of $^{116}$Cd
presented by Thibaud Le Noblet and Alberto Remoto at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
The SuperNemo $^{82}$Se-source foils radiopurity measurement with the BiPo-3 detector
presented by Pia Loaiza at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
Proceedings
The SuperNEMO Light Injection and Monitoring System
presented by Thibaud Le Noblet, John Cesar, Ramon Salazar at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
Proceedings
High resolution low background calorimeter for SuperNEMO
presented by Christine Marquet and Cedric Cerna at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
Proceedings
Development of an optical simulation for the SuperNEMO calorimeter
presented by Arnaud Huber at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
Proceedings
Construction, commissioning and transport of the tracker module for the SuperNEMO experiment
presented by Lauren Dawson, Ashwin Chopra and Michele Cascella at Neutrino 2016, 7 July 2016
Proceedings
SuperNEMO - a new generation of underground experiments for double beta-decay investigations: background constraints
presented by Pavel Povinec at Vienna Conference on Instrumentation, 15 February 2016
Measurement of extremely low radioactive contaminations for the SuperNEMO project
presented by Arnaud Chapon at Neutrino-Champagne, 5th International Workshop on Low Energy Neutrino Physics, 12 August 2010
The SuperNEMO experiment
presented by Federico Nova at Neutrino 2010, 14 June 2010
SuperNEMO - the next generation double beta decay experiment
presented by Irina Nasteva at EPS 2009, 22 July 2009
Proceedings
NEMO in the News
Find out what the world has to say about SuperNEMO and NEMO-3.
SuperNEMO, une expérience pour cerner la nature des neutrinos, from Le Monde, 26 November 2025
Depuis mi-octobre, ce détecteur situé à 1 700 mètres sous terre cherche un type de radioactivité jamais vu jusqu’alors.
How the SuperNEMO experiment could help solve the mystery of the origin of matter in the universe, from The Conversation, 24 November 2017
Deep beneath the Alpine ski slopes, patient scientists are waiting to observe a rare radioactive decay that would make us rewrite the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
Maurienne reportage #103 SuperNemo, from Maurienne TV, 21 November 2017
Cette semaine, dans Maurienne Reportage, Maurienne TV s'est rendu à Modane pour assister à l'inauguration du « SuperNemo », un détecteur de particules unique au monde. Bon Maurienne Reportage !
Un détecteur de particules unique au monde, fierté du Laboratoire souterrain de Modane, from La Maurienne, 16 November 2017
Non, il ne s’agit pas d’un poisson clown possédant des pouvoirs surnaturels… SuperNémo, tel est son nom, est un détecteur de particules qui, s’il n’a pas de pouvoirs surnaturels, a bien « une capacité technique unique au monde », assure Fabrice Piquemal, directeur du Laboratoire souterrain de Modane (LSM).
UK team probe the nature of the neutrino one mile underneath a mountain, from STFC, 09 November 2017
A mile beneath the French Alps scientists are hoping to unlock the mysteries of anti-matter and the neutrino particle.
Plongée au cœur des souterrains artificiels des Alpes, from France 3 Alpes, 28 February 2017
Ils ont été construits pour l'exploitation de ressources minières, la recherche sur les mystères de l'Univers ou la défense contre les bombardements alliés... Les Alpes du Nord regorgent de souterrains façonnés par l'homme. (Emission en français)

L'autre hypothèse : la particule de Majorana, from Sciences et Avenir, 01 October 2016
L'énigme de l'antimatière pourrait voir sa réponse surgir des montagnes situées à la frontière franco-italienne. Là, sous 1700 mètres de roches, le Laboratoire souterrain de Modane (LSM) est une oasis préservée des particules invisibles bombardant sans cesse la surface de la Terre et traversant notre corps chaque seconde. (Article en français)
How the particle that led Bohr to think energy might not be conserved could lead the next revolution in physics, from The Guardian, 18 October 2015
Neutrinos are ubiquitous, but mysterious. A Nobel prize was awarded this year for the discovery that they have mass, and undergo quantum oscillations as they travel - discoveries that fundamentally changed our understanding of physics and cosmology. A rare nuclear decay, being searched for now, might lead to a similar revolution...
NEMO closes in on neutrino mass, from phys.org, 20 June 2014
The NEMO (Neutrino Ettore Majorana Observatory) experiment, whose goal was to elucidate the nature of neutrinos and measure their mass, yielded very positive results. The product of an extensive international collaboration including seven CNRS joint laboratories1, the detector, installed in the Modane Underground Laboratory (CNRS/CEA) in the Fréjus road tunnel, ran from 2003 to 2011...

Interview de Fabrice Piquemal, porte-parole de SuperNEMO et directeur du LSM (en francais), from Radio France Internationale, 01 January 2009
Interview de Fabrice Piquemal, directeur du LSM par Dominique Desaunay de Radio France Internationale au labo en 2009...

Video - the lab as if you were there, from LSM, 01 January 2005
Video from 2005 of a visit to the LSM underground lab, where NEMO-3 was installed. 10 minutes, no narration.
SuperNEMO Papers
Journal papers from the SuperNEMO experiment.
Calorimeter commissioning of the SuperNEMO Demonstrator
JINST 20 (2025) T11003 (arXiv 2412.18021), 12 November 2025
Abstract
The SuperNEMO experiment is searching for neutrinoless double beta decay of $^{82}$Se, with the unique combination of a tracking detector and a segmented calorimeter. This feature allows to detect the two electrons emitted in the decay and measure their individual energy and angular distribution. The SuperNEMO calorimeter consists of 712 plastic scintillator blocks readout by large PMTs. After the construction of the demonstrator calorimeter underground, we have performed its first commissioning using γ-particles from calibration sources or from the ambient radioactive background. This article presents the quality assurance tests of the SuperNEMO demonstrator calorimeter and its first time and energy calibrations, with the associated methods.
Fabrication of thin planar radiopure foils with 82Se for the SuperNEMO Demonstrator
For submission to JINST (arXiv 2509.08931), 12 September 2025
Abstract
The SuperNEMO Demonstrator, designed to search for double beta decay using enriched $^{82}$Se, has been assembled in the Modane Underground Laboratory under the French Alps. Thin foils with radio - purified and enriched $^{82}$Se are installed centrally in the detector. A novel foil fabrication method has been developed, improving the radiopurity achieved in the previous generation experiment. It consists of wrapping standalone selenium pads in raw Mylar, combined with selenium purified by a new reverse-chromatography method. This paper describes the features of these foils, their fabrication process, the characterization results, and the integration of the foils into the SuperNEMO Demonstrator.
The impact of helium exposure on the PMTs of the SuperNEMO experiment
JINST 20 (2025) P06018 (arXiv 2501.13755), 17 June 2025
Abstract
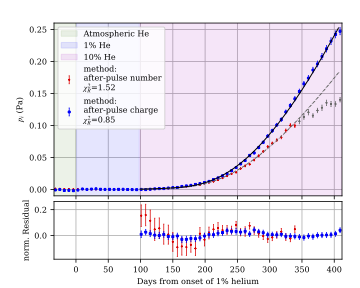
The performance of Hamamatsu 8” photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) of the type used in the SuperNEMO neutrinoless double-beta decay experiment (R5912-MOD), is investigated as a function of exposure to helium (He) gas. Two PMTs were monitored for over a year, one exposed to varying concentrations of He, and the other kept in standard atmospheric conditions as a control. Both PMTs were exposed to light signals generated by a $^{207}$Bi radioactive source coupled to a plastic scintillator, which provided consistent large input PMT signals similar to those that are typical of the SuperNEMO experiment. The energy resolution of PMT signals corresponding to 1 MeV energy scale determined from the $^{207}$Bi decay spectrum, shows a negligible degradation with He exposure; however the rate of after-pulsing shows a clear increase with He exposure, which is modelled and compared to diffusion theory. A method for reconstructing the partial pressure of He within the PMT and a method for determining the He breakdown point, are introduced. The implications for long-term SuperNEMO operations are briefly discussed.
Measurement of the distribution of $^{207}$Bi depositions on calibration sources for SuperNEMO
JINST 16 (2021) T07012 (arXiv 2103.14429), 23 July 2021
Abstract
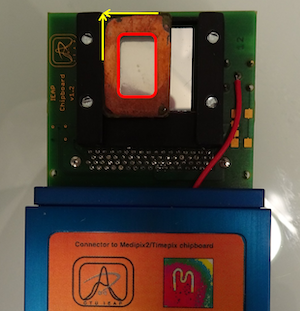
The SuperNEMO experiment will search for neutrinoless double-beta decay ($0\nu\beta\beta$), and study the Standard-Model double-beta decay process ($2\nu\beta\beta$). The SuperNEMO technology can measure the energy of each of the electrons produced in a double-beta ($\beta\beta$) decay, and can reconstruct the topology of their individual tracks. The study of the double-beta decay spectrum requires very accurate energy calibration to be carried out periodically. The SuperNEMO Demonstrator Module will be calibrated using 42 calibration sources, each consisting of a droplet of $^{207}$Bi within a frame assembly. The quality of these sources, which depends upon the entire $^{207}$Bi droplet being contained within the frame, is key for correctly calibrating SuperNEMO's energy response. In this paper, we present a novel method for precisely measuring the exact geometry of the deposition of $^{207}$Bi droplets within the frames, using Timepix pixel detectors. We studied 49 different sources and selected 42 high-quality sources with the most central source positioning.
Development of methods for the preparation of radiopure 82Se sources for the SuperNEMO neutrinoless double-beta decay experiment
Radiochimica Acta, 108 (2020) 11 , 14 February 2020
Abstract
A radiochemical method for producing 82Se sources with an ultra-low level of contamination of natural radionuclides (40K, decay products of 232Th and 238U) has been developed based on cation-exchange chromatographic purification with reverse removal of impurities. It includes chromatographic separation (purification), reduction, conditioning (which includes decantation, centrifugation, washing, grinding, and drying), and 82Se foil production. The conditioning stage, during which highly dispersed elemental selenium is obtained by the reduction of purified selenious acid (H2SeO3) with sulfur dioxide (SO2) represents the crucial step in the preparation of radiopure 82Se samples. The natural selenium (600 g) was first produced in this procedure in order to refine the method. The technique developed was then used to produce 2.5 kg of radiopure enriched selenium (82Se). The produced 82Se samples were wrapped in polyethylene (12 μm thick) and radionuclides present in the sample were analyzed with the BiPo-3 detector. The radiopurity of the plastic materials (chromatographic column material and polypropylene chemical vessels), which were used at all stages, was determined by instrumental neutron activation analysis. The radiopurity of the 82Se foils was checked by measurements with the BiPo-3 spectrometer, which confirmed the high purity of the final product. The measured contamination level for 208Tl was 8-54 μBq/kg, and for 214Bi the detection limit of 600 μBq/kg has been reached.
Calorimeter development for the SuperNEMO double beta decay experiment
Nucl.Inst.Meth. A 868 98-108 (arXiv 1707.06823), 01 October 2017
Abstract
SuperNEMO is a double-$\beta$ decay experiment, which will employ the successful tracker–calorimeter technique used in the recently completed NEMO-3 experiment. SuperNEMO will implement 100 kg of double-$\beta$ decay isotope, reaching a sensitivity to the neutrinoless double-$\beta$ decay ($0\nu\beta\beta$) half-life of the order of $10^{26}$ yr, corresponding to a Majorana neutrino mass of 50–100 meV. One of the main goals and challenges of the SuperNEMO detector development programme has been to reach a calorimeter energy resolution, $\Delta E/E$, around $3\% / \sqrt{E}$ (MeV) $\sigma$, or $7\% / \sqrt{E}$ (MeV) FWHM (full width at half maximum), using a calorimeter composed of large volume plastic scintillator blocks coupled to photomultiplier tubes. We describe the R&D programme and the final design of the SuperNEMO calorimeter that has met this challenging goal.
The BiPo-3 detector for the measurement of ultra low natural radioactivities of thin materials
JINST 12 (2017) P06002 (arXiv 1005.0343), 01 June 2017
Abstract
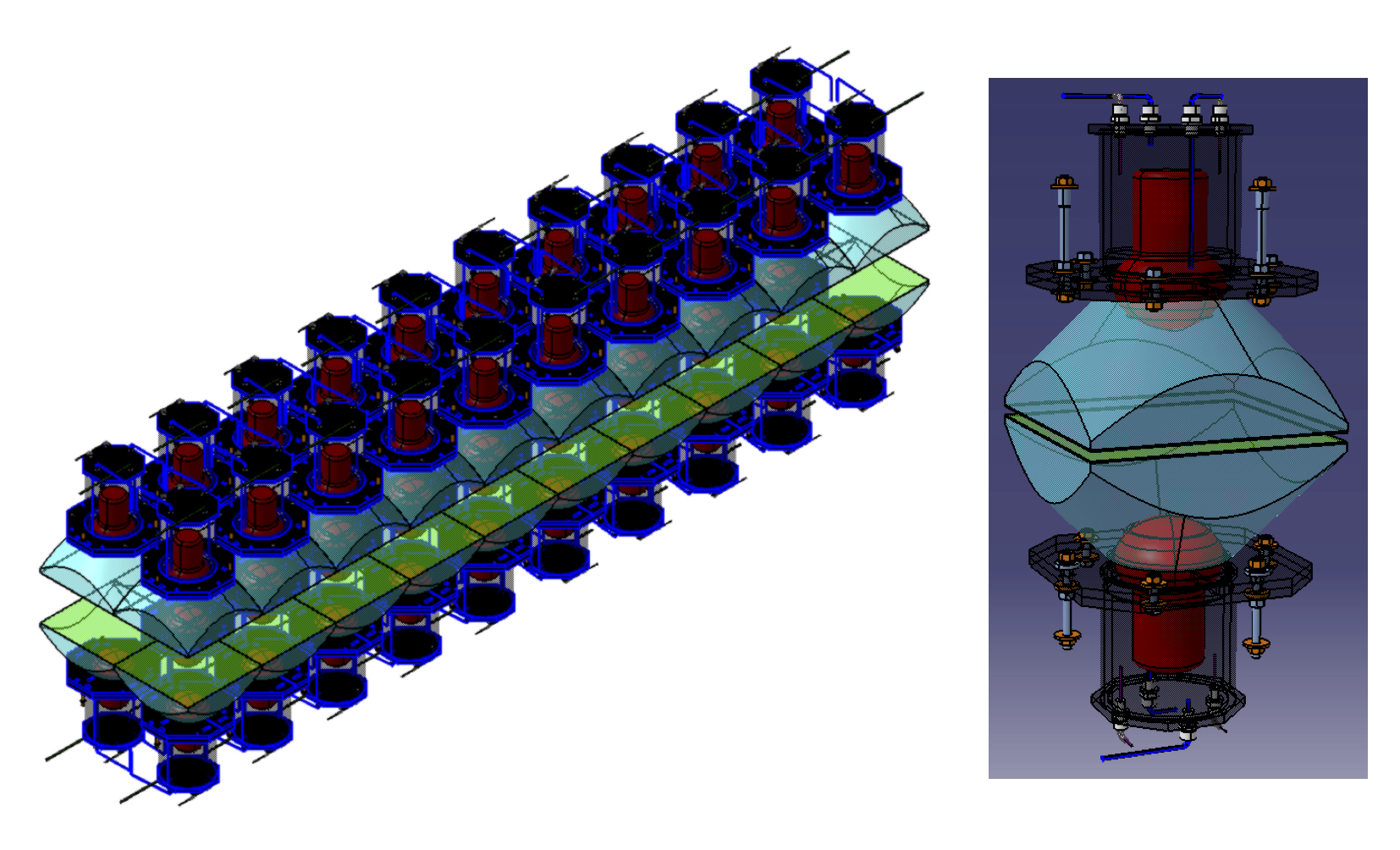
The BiPo-3 detector, running at the Canfranc Underground Laboratory (Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc, LSC, Spain) since 2013, is a low-radioactivity detector dedicated to measuring ultra low natural radionuclide contaminations of $^{208}$Tl ($^{232}$Th chain) and $^{214}$Bi ($^{238}$U chain) in thin materials. The total sensitive surface area of the detector is 3.6m$^2$. The detector has been developed to measure the radiopurity of the selenium double $\beta$-decay source foils of the SuperNEMO experiment. In this paper the design and performance of the detector, and results of the background measurements in $^{208}$Tl and $^{214}$Bi, are presented, and the validation of the BiPo-3 measurement with a calibrated aluminium foil is discussed. Results of the $^{208}$Tl and $^{214}$Bi activity measurements of the first enriched $^{82}$Se foils of the double $\beta$-decay SuperNEMO experiment are reported. The sensitivity of the BiPo-3 detector for the measurement of the SuperNEMO $^{82}$Se foils is $\mathcal{A}$($^{208}$Tl) $<2$ $\mu$Bq/kg (90% C.L.) and $\mathcal{A}$($^{214}$Bi) $<140$ $\mu$Bq/kg (90% C.L.) after 6 months of measurement.
Construction and commissioning of the SuperNEMO detector tracker
Nucl.Inst.Meth. A (2016) 824 507-509 , 11 July 2016
Abstract
The SuperNEMO detector will search for neutrinoless double beta decay at the Modane Underground Laboratory; the detector design allows complete topological reconstruction of the decay event enabling excellent levels of background rejection and, in the event of a discovery, the ability to determine the nature of the lepton number violating process. In order to demonstrate the feasibility of the full experiment, we are building a Demonstrator Module containing 7 kg of $^{82}$Se, with an expected sensitivity of |$m_{\beta\beta}$| < 0.2 - 0.4 eV after 2.5 yr. The demonstrator tracker is currently being assembled in the UK; the main challenge in the tracker design is the high radiopurity required to limit the background. For this reason the cell wiring is automated and every step of the tracker assembly happens in a clean environment. All components are carefully screened for radiopurity and each section of the tracker, once assembled, is sealed and checked for Radon emanation. We present the detector design, the current status of the construction and present the first results from the surface commissioning of one section of the Demonstrator Module tracker.
Spectral modeling of scintillator for the NEMO-3 and SuperNEMO detectors
Nucl.Inst.Meth. A 625(1) 20-28 (arXiv 1004.3779), 01 January 2011
Abstract
We have constructed a GEANT4-based detailed software model of photon transport in plastic scintillator blocks and have used it to study the NEMO-3 and SuperNEMO calorimeters employed in experiments designed to search for neutrinoless double beta decay. We compare our simulations to measurements using conversion electrons from a calibration source of $^{207}$Bi and show that the agreement is improved if wavelength-dependent properties of the calorimeter are taken into account. In this article, we briefly describe our modeling approach and results of our studies.
Probing new physics models of neutrinoless double beta decay with SuperNEMO
Eur. Phys. J. C (2010) 70: 927. (arXiv 1005.1241), 18 November 2010
Abstract
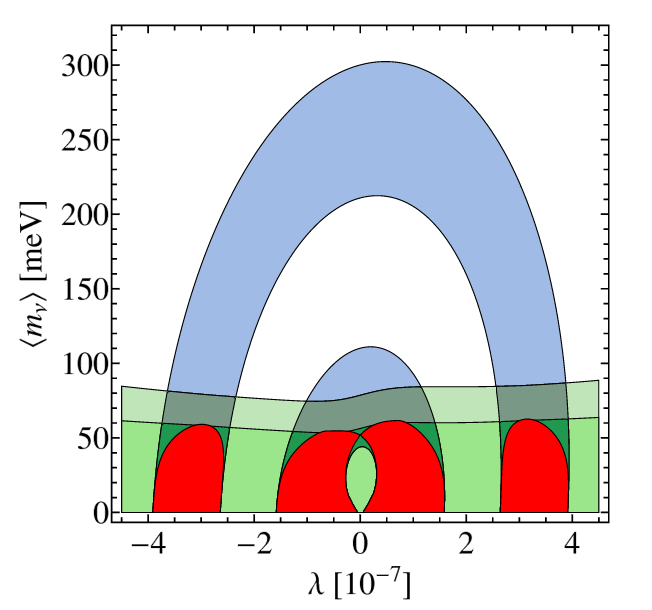
The possibility to probe new physics scenarios of light Majorana neutrino exchange and right-handed currents at the planned next generation neutrinoless double $\beta$ decay experiment SuperNEMO is discussed. Its ability to study different isotopes and track the outgoing electrons provides the means to discriminate different underlying mechanisms for the neutrinoless double $\beta$ decay by measuring the decay half-life and the electron angular and energy distributions.
Results of the BiPo-1 prototype for radiopurity measurements for the SuperNEMO double beta decay source foils
Nucl.Inst.Meth. A 622(1) 120–128 (arXiv 1005.0343), 01 October 2010
Abstract
The development of BiPo detectors is dedicated to the measurement of extremely high radiopurity in $^{208}$Tl and $^{214}$Bi for the SuperNEMO double beta decay source foils. A modular prototype, called BiPo-1, with 0.8 m$^2$ of sensitive surface area, has been running in the Modane Underground Laboratory since February, 2008. The goal of BiPo-1 is to measure the different components of the background and in particular the surface radiopurity of the plastic scintillators that make up the detector. The first phase of data collection has been dedicated to the measurement of the radiopurity in $^{208}$Tl. After more than one year of background measurement, a surface activity of the scintillators of $\mathcal{A}(^{208}\textrm{Tl})=1.5\mu$ Bq/m$^2$ is reported here. Given this level of background, a larger BiPo detector having 12 m$^2$ of active surface area, is able to qualify the radiopurity of the SuperNEMO selenium double beta decay foils with the required sensitivity of $\mathcal{A}(^{208}\textrm{Tl})<2\mu$ Bq/kg (90% C.L.) with a six month measurement.
The SuperNEMO project
Physics of Atomic Nuclei, Volume 69, Issue 12, pp.2096-2100 , 23 November 2005
Abstract
Neutrinoless double-beta decay ($\beta\beta (0 \nu)$) is the most sensitive process in the search for leptonic number violation and its discovery would prove that the neutrino is a Majorana particle. From the experience of the NEMO-3 detector construction and data analysis, the NEMO Collaboration proposes a three-year R&D program in order to design a detector (SuperNEMO) sensitive to a $\beta\beta (0 \nu)$ period of few 10$^{26}$ yr coupling track reconstruction and calorimeter.
NEMO-3 Papers
Papers from SuperNEMO's predescessor, NEMO-3.
Measurement of double beta decay of $^{150}$Nd to the $0^{+}_{1}$ excited state of $^{150}$Sm in NEMO-3
Eur. Phys. J.C. 83 (2023) 12, 1117 (arXiv 2203.03356), 09 December 2023
Abstract
NEMO-3 results for the double beta decay of $^{150}$Nd to the $0^{+}_{1}$ and $2^{+}_{1}$ excited states of $^{150}$Sm are reported. The data recorded during $5.25$ y with $36.6$ g of the isotope $^{150}$Nd were used in the analysis. For the first time the signal of $2$νββ transition to the $0^{+}_{1}$ excited state is detected with statistical significance exceeding $5$ sigma. The half-life is measured to be $T^{2νββ}_{1/2}(0^{+}_{1})=[1.11^{+0.19}_{−0.14}(stat)^{+0.17}_{−0.15}(syst)]×10^{20}$y. Limits are set on $2$νββ decay to $2^{+}_{1}$ level and on $0$νββ decay to $0^{+}_{1}$ and $2^{+}_{1}$ levels of $^{150}$Sm.
Search for Periodic Modulations of the Rate of Double-Beta Decay of $^{100}$Mo in the NEMO-3 Detector
Phys. Rev. C 104, L061601 (2021) (arXiv 2011.07657), 15 November 2020
Abstract
Double-beta decays of $^{100}$Mo from the 6.0195-year exposure of a 6.914 kg high-purity sample were recorded by the NEMO-3 experiment that searched for neutrinoless double-beta decays. These ultra-rare transitions to $^{100}$Ru have a half-life of approximately $7\times10^{18}$ years, and have been used to conduct the first ever search for periodic variations of this decay mode. The Lomb-Scargle periodogram technique, and its error-weighted extension, were employed to look for periodic modulations of the half-life. Monte Carlo modeling was used to study the modulation sensitivity of the data over a broad range of amplitudes and frequencies. Data show no evidence of modulations with amplitude greater than 2.5% in the frequency range of 0.33225y$^{−1}$ to 365.25y$^{−1}$.
Search for the double-beta decay of $^{82}Se$ to the excited states of $^{82}$Kr with NEMO-3
Nucl. Phys. A 996, 121701 (arXiv 2001.06388), 01 April 2020
Abstract

The double-beta decay of $^{82}$Se to the 0$^+_1$ excited state of $^{82}$Kr has been studied with the NEMO-3 detector using 0.93 kg of enriched $^{82}$Se measured for 4.75 y, corresponding to an exposure of 4.42 kg y. A dedicated analysis to reconstruct the gamma-rays has been performed to search for events in the $2e2\gamma$ channel. No evidence of a $2\nu\beta\beta$ decay to the 0$^+_1$ state has been observed and a limit of $T^{2\nu}_{ 1/2}(^{82}\text{Se}; 0^+_{\text{gs}}\to 0^+_1) > 1.3 \times 10^{21}$ y at 90% CL has been set. Concerning the $0\nu\beta\beta$ decay to the 0$^+_1$ state, a limit for this decay has been obtained with $T^{0\nu}_{ 1/2}(^{82}\text{Se}; 0^+_{\text{gs}}\to 0^+_1) > 2.3 \times 10^{22}$ y at 90% CL, independently from the $2\nu\beta\beta$ decay process. These results are obtained for the first time with a tracko-calo detector, reconstructing every particle in the final state.
Detailed studies of $^{100}$Mo two-neutrino double beta decay in NEMO-3
Eur. Phys. J. C (2019) 79: 440 (arXiv 1903.08084), 24 May 2019
Abstract

The full data set of the NEMO-3 experiment has been used to measure the half-life of the two-neutrino double beta decay of $^{100}$Mo to the ground state of $^{100}$Ru, $T_{1/2} = \left[ 6.81 \pm 0.01\,\left(\mbox{stat}\right) ^{+0.38}_{-0.40}\,\left(\mbox{syst}\right) \right] \times10^{18}$ y. The two-electron energy sum, single electron energy spectra and distribution of the angle between the electrons are presented with an unprecedented statistics of $5\times10^5$ events and a signal-to-background ratio of $\sim$80. Clear evidence for the Single State Dominance model is found for this nuclear transition. Limits on Majoron emitting neutrinoless double beta decay modes with spectral indices of n=2,3,7, as well as constraints on Lorentz invariance violation and on the bosonic neutrino contribution to the two-neutrino double beta decay mode are obtained.
Final results on $^{82}$Se double beta decay to the ground state of $^{82}$Kr from the NEMO-3 experiment
Eur. Phys. J. C (2018) 78: 821 (arXiv 1806.05553), 16 October 2018
Abstract

Using data from the NEMO-3 experiment, we have measured the two-neutrino double beta decay ($2\nu\beta\beta$) half-life of $^{82}$Se as $T_{1/2}^{2\nu} (9.39 \pm 0.17\,\left(\mbox{stat}\right) \pm 0.58\,\left(\mbox{syst}\right)) \times 10^{19}$y under the single-state dominance hypothesis for this nuclear transition. The corresponding nuclear matrix element is $\left|M^{2\nu}\right| = 0.0498 \pm 0.0016$. In addition, a search for neutrinoless double beta decay ($0\nu\beta\beta$) using 0.93 kg of $^{82}$Se observed for a total of 5.25 y has been conducted and no evidence for a signal has been found. The resulting half-life limit of $T_{1/2}^{0\nu} > 2.5 \times 10^{23} \,\mbox{y} \,(90\%\,\mbox{C.L.})$ for the light neutrino exchange mechanism leads to a constraint on the effective Majorana neutrino mass of $\langle m_{\nu} \rangle < \left(1.2 - 3.0\right) \,\mbox{eV}$, where the range reflects $0\nu\beta\beta$ nuclear matrix element values from different calculations. Furthermore, constraints on lepton number violating parameters for other $0\nu\beta\beta$ mechanisms, such as right-handed currents, majoron emission and R-parity violating supersymmetry modes have been set.
Search for Neutrinoless Quadruple-β Decay of $^{150}$Nd with the NEMO-3 Detector
Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 041801 (arXiv 1705.08847), 24 July 2017
Abstract
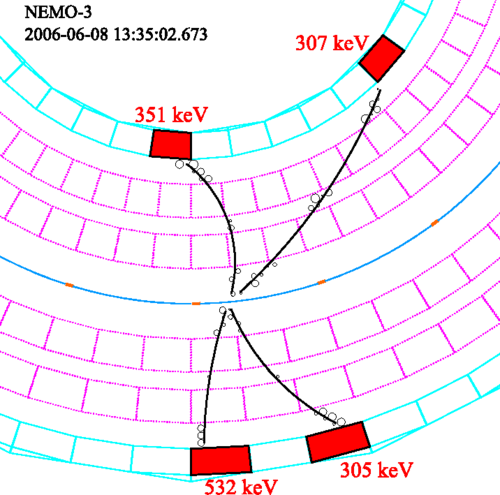
We report the results of a first experimental search for lepton number violation by four units in the neutrinoless quadruple-$\beta$ decay of $^{150}$Nd using a total exposure of $0.19$ kg$\cdot$y recorded with the NEMO-3 detector at the Modane Underground Laboratory (LSM). We find no evidence of this decay and set lower limits on the half-life in the range $T_{1/2}>(1.1\text{-}3.2)\times10^{21}$ y at the $90\%$ CL, depending on the model used for the kinematic distributions of the emitted electrons.
Measurement of the 2νββ decay half-life and search for the 0νββ decay of 116Cd with the NEMO-3 detector
Phys. Rev. D 95, 012007 (arXiv 1610.03226), 17 January 2017
Abstract
The NEMO-3 experiment measured the half-life of the 2$\nu\beta\beta$ decay and searched for the 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decay of $^{116}$Cd. Using 410 g of $^{116}$Cd installed in the detector with an exposure of 5.26 y, (4968$\pm$74) events corresponding to the 2$\nu\beta\beta$ decay of $^{116}$Cd to the ground state of $^{116}$Sn have been observed with a signal to background ratio of about 12. The half-life of the 2$\nu\beta\beta$ decay has been measured to be $T^{2\nu}_{1/2} = \left[2.74 \pm 0.04(\textrm{stat}) \pm0.18 (\textrm{syst})\right]\times 10^{19}$ y. No events have been observed above the expected background while searching for 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decay. The corresponding limit on the half-life is determined to be $T_{1/2}^{0\nu}\geq 1.0\times 10^{23}$ y at the 90 C.L. which corresponds to an upper limit on the effective Majorana neutrino mass of $\left < m_\nu \right > \leq 1.4-2.5$ eV depending on the nuclear matrix elements considered. Limits on other mechanisms generating 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decay such as the exchange of R-parity violating supersymmetric particles, right-handed currents and majoron emission are also obtained.
Measurement of the 2νββ decay half-life of $^{150}$Nd and a search for 0νββ decay processes with the full exposure from the NEMO-3 detector
Phys. Rev. D 94, 072003 (arXiv 1606.08494), 11 October 2016
Abstract
We present results from a search for neutrinoless double-$\beta$(0$\nu\beta\beta$) decay using 36.6 g of the isotope $^{150}$Nd with data corresponding to a live time of 5.25 y recorded with the NEMO-3 detector. We construct a complete background model for this isotope, including a measurement of the two-neutrino double-$\beta$ decay half-life of $T^{2\nu}_{1/2} = \left[9.34 \pm 0.22(\textrm{stat})+0.62-0.60 (\textrm{syst})\right]\times 10^{18}$ y for the ground state transition, which represents the most precise result to date for this isotope. We perform a multivariate analysis to search for 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decays in order to improve the sensitivity and, in the case of observation, disentangle the possible underlying decay mechanisms. As no evidence for 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decay is observed, we derive lower limits on half-lives for several mechanisms involving physics beyond the standard model. The observed lower limit, assuming light Majorana neutrino exchange mediates the decay, is $T_{1/2}^{0\nu}\geq 2.0\times 10^{22}$ y at the 90% C.L., corresponding to an upper limit on the effective neutrino mass of $\left < m_\nu \right > \leq 1.6-5.3$ eV.
Measurement of the double-beta decay half-life and search for the neutrinoless double-beta decay of $^{48}$Ca with the NEMO-3 detector
Phys. Rev. D 93, 112008 (arXiv 1604.01710), 14 June 2016
Abstract
The NEMO-3 experiment at the Modane Underground Laboratory investigates the double-beta decay of $^{48}$Ca. Using 5.25 yr of data recorded with a 6.99 g sample of $^{48}$Ca, approximately 150 double-beta decay candidate events are selected with a signal-to-background ratio greater than 3. The half-life for the two-neutrino double-beta decay of $^{48}$Ca is measured to be $T^{2\nu}_{1/2} = \left[6.4 ^{+0.7}_{-0.6}(\textrm{stat})^{+1.2}_{-0.9} (\textrm{syst})\right]\times 10^{19}$ yr. A search for neutrinoless double-beta decay of $^{48}$Ca yields a null result, and a corresponding lower limit on the half-life is found to be $T_{1/2}^{0\nu}\geq 2.0\times 10^{22}$ at 90% confidence level, translating into an upper limit on the effective Majorana neutrino mass of $\left < m_{\beta\beta} \right > \leq 6.0-26$ eV, with the range reflecting different nuclear matrix element calculations. Limits are also set on models involving Majoron emission and right-handed currents.
Results of the search for neutrinoless double-β decay in $^{100}$Mo with the NEMO-3 experiment
Phys. Rev. D 92, 072011 (arXiv 1506.05825), 21 October 2015
Abstract
The NEMO-3 detector, which had been operating in the Modane Underground Laboratory from 2003 to 2010, was designed to search for neutrinoless double-$\beta$(0$\nu\beta\beta$) decay. We report the final results of a search for 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decays with 6.914 kg of $^{100}$Mo using the entire NEMO-3 data set with a detector live time of 4.96 yr, which corresponds to an exposure of 34.3 kg yr. We perform a detailed study of the expected background in the 0$\nu\beta\beta$ signal region and find no evidence of 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decays in the data. The level of observed background in the 0$\nu\beta\beta$ signal region $[2.8–3.2]$ MeV is $0.44\pm0.13$ counts/yr/kg, and no events are observed in the interval $[3.2–10]$ MeV. We therefore derive a lower limit on the half-life of 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decays in $^{100}$Mo of $T_{1/2}(0$\nu\beta\beta$)> 1.1\times 10^{24}$ yr at the 90% confidence level, under the hypothesis of decay kinematics similar to that for light Majorana neutrino exchange. Depending on the model used for calculating nuclear matrix elements, the limit for the effective Majorana neutrino mass lies in the range $\left < m_\nu \right > \leq 0.33-0.62$ eV. We also report constraints on other lepton-number violating mechanisms for 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decays.
Search for neutrinoless double-beta decay of $^{100}$Mo with the NEMO-3 detector
Phys. Rev. D 89, 111101(R) (arXiv 1506.05825), 12 June 2014
Abstract
We report the results of a search for the neutrinoless double-$\beta$ decay (0$\nu\beta\beta$) of $^{100}$Mo, using the NEMO-3 detector to reconstruct the full topology of the final state events. With an exposure of 34.7 kg y, no evidence for the 0$\nu\beta\beta$ signal has been found, yielding a limit for the light Majorana neutrino mass mechanism of $T_{1/2}^{0\nu}> 1.1\times 10^{24}$ years (90% C.L.) once both statistical and systematic uncertainties are taken into account. Depending on the nuclear matrix elements this corresponds to an upper limit on the Majorana effective neutrino mass of $\left < m_\nu \right > < 0.3-0.9$ eV (90% C.L.). Constraints on other lepton number violating mechanisms of 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decays are also given. Searching for high-energy double electron events in all suitable sources of the detector, no event in the energy region [3.2–10] MeV is observed for an exposure of $47 \textrm{kg}\cdot\textrm{y}$.
Investigation of double beta decay of $^{100}$Mo to excited states of $^{100}$Ru
Nucl. Phys. A 925 (2014) 25 (arXiv 1402.7196), 07 February 2014
Abstract
Double beta decay of $^{100}$Mo to the excited states of daughter nuclei has been studied using a 600 cm$^3$ low-background HPGe detector and an external source consisting of 2588 g of 97.5% enriched metallic $^{100}$Mo, which was formerly inside the NEMO-3 detector and used for the NEMO-3 measurements of $^{100}$Mo. The half-life for the two-neutrino double beta decay of $^{100}$Mo to the excited $0_1^+$ state in $^{100}$Ru is measured to be $T_{1/2} = \left[7.5 \pm 0.6(\textrm{stat})\pm 0.6 (\textrm{syst})\right]\cdot 10^{20}$ yr. For other ($0\nu + 2 \nu$) transitions to the $2_1^+$, $2_2^+$, $0_2^+$, $2_3^+$ and $0_3^+$ levels in $^{100}$Ru, limits are obtained at the level of $~(0.25-1.1)\cdot 10^{22}$ yr.
Measurement of the ββ Decay Half-Life of $^{130}$Te with the NEMO-3 Detector
Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 062504 (arXiv 1104.3716), 04 August 2011
Abstract
We report results from the NEMO-3 experiment based on an exposure of 1275 days with 661 g of $^{130}$Te in the form of enriched and natural tellurium foils. The $\beta\beta$ decay rate of $^{130}$Te is found to be greater than zero with a significance of 7.7 standard deviations and the half-life is measured to be $T^{2\nu}_{1/2} = \left[7.0 \pm 0.9(\textrm{stat})\pm 1.1 (\textrm{syst})\right]\times 10^{20} \textrm{yr}$. This represents the most precise measurement of this half-life yet published and the first real-time observation of this decay.
Measurement of the two neutrino double beta decay half-life of Zr-96 with the NEMO-3 detector
Nucl.Phys.A847:168-179 (arXiv 0906.2694), 08 December 2010
Abstract
Using 9.4 g of $^{96}$Zr isotope and 1221 days of data from the NEMO-3 detector corresponding to 0.031 kg y, the obtained 2$\nu\beta\beta$ decay half-life measurement is $T^{2\nu}_{1/2} = \left[2.35 \pm 0.14(\textrm{stat})\pm0.16 (\textrm{syst})\right]\times 10^{19} \textrm{yr}$.Different characteristics of the final state electrons have been studied, such as the energy sum, individual electron energy, and angular distribution. The 2$\nu$ nuclear matrix element is extracted using the measured 2$\nu\beta\beta$ half-life and is $M^{2\nu}=0.049\pm0.002$. Constraints on 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decay have also been set.
Measurement of the Double Beta Decay Half-life of $^{150}$Nd and Search for Neutrinoless Decay Modes with the NEMO-3 Detector
Phys. Rev. C 80, 032501(R) (arXiv 0810.0248), 03 September 2009
Abstract
The half-life for double-$\beta$ decay of $^{150}$Nd has been measured by the NEMO-3 experiment at the Modane Underground Laboratory. Using 924.7 days of data recorded with 36.55g of $^{150}$Nd, we measured the half-life for 2$\nu\beta\beta$ decay to be $T^{2\nu}_{1/2} = \left[9.11 ^{+0.25}_{-0.22}(\textrm{stat})\pm0.63 (\textrm{syst})\right]\times 10^{18} \textrm{yr}$. The observed limit on the half-life for neutrinoless double-$\beta$ decay is found to be $T_{1/2}^{0\nu}>1.8\times 10^{22}$ yr at 90% confidence level. This translates into a limit on the effective Majorana neutrino mass of $\left < m_\nu \right > <4.0-6.3$ eV if the nuclear deformation is taken into account. We also set limits on models involving Majoron emission, right-handed currents, and transitions to excited states.
Measurement of the background in the NEMO 3 double beta decay experiment
Nucl. Inst. Meth. A 606, Issue 3 449-465 (arXiv 0903.2277), 21 July 2009
Abstract
In the double beta decay experiment NEMO 3 a precise knowledge of the background in the signal region is of outstanding importance. This article presents the methods used in NEMO 3 to evaluate the backgrounds resulting from most if not all possible origins. It also illustrates the power of the combined tracking-calorimetry technique used in the experiment.
Measurement of double beta decay of $^{100}$Mo to excited states in the NEMO 3 experiment
Nucl. Phys. A 781 209-226 (arXiv hep-ex/0609058), 01 January 2007
Abstract
The double beta decay of $^{100}$Mo to the $0_1^+$ and $2_1^+$ excited states of $^{100}$Ru is studied using the NEMO 3 data. After the analysis of 8024 h of data the half-life for the two-neutrino double beta decay of $^{100}$Mo to the excited $0_1^+$ state is measured to be $T^{2\nu}_{1/2} = \left[5.7 ^{+1.3}_{-0.9}(\textrm{stat})\pm0.8 (\textrm{syst})\right]\times 10^{20} \textrm{y}$. The signal-to-background ratio is equal to 3. Information about energy and angular distributions of emitted electrons is also obtained. No evidence for neutrinoless double beta decay to the excited $0_1^+$ state has been found. The corresponding half-life limit is $T_{1/2}^{(0\nu)}(0^+ \to 0_1^+)>8.9\times 10^{22}$ y (at 90% C.L.). The search for the double beta decay to the $2_1^+$ excited state has allowed the determination of limits on the half-life for the two neutrino mode $T_{1/2}^{(2\nu)}(0^+ \to 2_1^+)>1.1\times 10^{21}$ y (at 90% C.L.) and for the neutrinoless mode $T_{1/2}^{(0\nu)}(0^+ \to 2_1^+)>1.6\times 10^{23}$ y (at 90% C.L.).
Limits on different Majoron decay modes of $^{100}$Mo and $^{82}$Se for neutrinoless double beta decays in the NEMO-3 experiment
Nucl.Phys. A 765 (2006) 483-494 (arXiv hep-ex/0601021), 06 February 2006
Abstract
The NEMO-3 tracking detector is located in the Fréjus Underground Laboratory. It was designed to study double beta decay in a number of different isotopes. Presented here are the experimental half-life limits on the double beta decay process for the isotopes $^{100}$Mo and $^{82}$Se for different majoron emission modes and limits on the effective neutrino–majoron coupling constants. In particular, new limits on “ordinary” majoron (spectral index 1) decay of $^{100}$Mo $(T_{1/2}>2.7\times 10^{22}\textrm{yr})$ and $^{82}$Se $(T_{1/2}>1.5\times 10^{22}\textrm{yr})$ have been obtained. Corresponding bounds on the majoron–neutrino coupling constant are $\left < g_{ee} \right > <0.4-1.8\times 10^{-4}$ and $<0.66-1.9\times 10^{-4}$.
First Results of the Search for Neutrinoless Double-Beta Decay with the NEMO 3 Detector
Phys. Rev. Let. 95, 182302 (arXiv hep-ex/0507083), 25 October 2005
Abstract
The NEMO 3 detector, which has been operating in the Fréjus underground laboratory since February 2003, is devoted to the search for neutrinoless double beta decay ($\beta\beta$0$\nu$). The half-lives of the two neutrino double beta decay ($\beta\beta 2 \nu$) have been measured for $^{100}$Mo and $^{82}$Se. After 389 effective days of data collection from February 2003 until September 2004 (Phase~I), no evidence for neutrinoless double beta decay was found from $\sim$7 kg of $^{100}$Mo and $\sim$1 kg of $^{82}$Se. The corresponding lower limits for the half-lives are $4.6 \times 10^{23}$ years for $^{100}$Mo and $1.0 \times 10^{23}$ years for $^{82}$Se (90\% C.L.). Depending on the nuclear matrix element calculation, the limits for the effective Majorana neutrino mass are $\langle m_{\nu} \rangle < 0.7-2.8$ eV for $^{100}$Mo and $\langle m_{\nu} \rangle < 1.7-4.9$ eV for $^{82}$Se.
Technical design and performance of the NEMO 3 detector
Nucl. Inst. Meth. A536 79-122 (arXiv physics/0402115), 01 January 2005
Abstract

The development of the NEMO 3 detector, which is now running in the Fréjus Underground Laboratory (L.S.M. Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane), was begun more than ten years ago. The NEMO 3 detector uses a tracking-calorimeter technique in order to investigate double beta decay processes for several isotopes. The technical description of the detector is followed by the presentation of its performance.
Possible background reductions in double beta decay experiments
Nucl.Instrum.Meth.A503:649-657 (arXiv nucl-ex/0302022), 11 May 2003
Abstract

The background induced by radioactive impurities of $^{208}\rm Tl$ and $^{214}\rm Bi$ in the source of the double beta experiment NEMO-3 has been investigated. New methods of data analysis which decrease the background from the above mentioned contamination are identified. The techniques can also be applied to other double beta decay experiments capable of measuring independently the energies of the two electrons.
Chemical purification of molybdenum samples for the NEMO 3 experiment
Nucl. Inst. Meth. A 474 93 , 21 November 2001
Abstract
Most currently, viable double beta decay experiments require highly enriched isotopic sources. These sources must be extraordinarily free of radioactive contamination. The double beta decay experiment NEMO 3 will study $^{100}$Mo, for which physical and chemical purification techniques have been investigated. The success of the chemical purification process is discussed in the context of ultra-low background, high-purity germanium spectrometer measurements.
SuperNEMO and NEMO-3 PhD Theses
Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Identification of Double Beta Decay Events in the SuperNEMO Experiment
Dr Matteo Ceschia
UCL, 2024, supervised by Ruben Saakyan and Cheryl Patrick
Studying the effects of alternative magnetic field configurations on the sensitivity of the SuperNEMO demonstrator to the 0$\nu\beta\beta$ decay of 82Se
Dr Hamzah Hussain
UCL, 2023, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Commissioning and Sensitivity Studies for the SuperNEMO Demonstrator Module
Dr Lauren Dawson
UCL, 2023, supervised by David Waters
The sensitivity of the NEMO technique to neutrinoless double beta decay and the commissioning of the SuperNEMO demonstrator module
Dr William Quinn
UCL, 2023, supervised by David Waters
Search for neutrinoless double beta decay of 82Se with the SuperNEMO experiment : reconstruction of the energy measured with the calorimeter and analysis of the first data from the demonstrator
Dr Xalbat Aguerre
University of Bordeaux / LP2IB, 2023, supervised by Emmanuel Chauveau and Christine Marquet
Characterization of the Timing Properties of the SuperNEMO Demonstrator. Extraction of the SuperNEMO Sensitivity to the Axial-Vector Coupling Constant
Dr Malak Hoballah
IJC Lab, 2022, supervised by Laurent Simard
Monte Carlo Simulations of Detectors Background and Analysis of Background Characteristics of the SuperNEMO Experiment in the Modane Underground Laboratory
Dr Veronika Palušová
Comenius University in Bratislava / University of Bordeaux, 2021, supervised by Pavel Povinec and Fabrice Piquemal
Calibration and monitoring systems for neutrinoless double beta decay searches in the SuperNEMO experiment
Dr Ramón Salazar
University of Texas at Austin, 2021, supervised by Karol Lang
Optimisation de la reconstruction gamma de l'expérience SuperNEMO en vue de l'étude du bruit de fond. Développement d'un détecteur sphérique proportionnel pour l'étude du radon dans l'expérience SuperNEMO
Dr Hichem Tedjditi
University of Aix-Marseille/CPPM, 2021, supervised by José Busto
Radon Background Studies for the SuperNEMO Experiment
Dr Fang Xie
UCL, 2020, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Étude de l’influence de la réjection du bruit de fond 208Tl sur la sensibilité à la 0νββ; caractérisation des performances en temps du calorimètre du démonstrateur SuperNEMO
Dr Cloé Girard-Carillo
Université Paris-Saclay / IJCLab, 2020, supervised by Laurent Simard and Mathieu Bongrand
Recherche de la nature du neutrino via la décroissance double bêta sans émission de neutrinos : Caractérisation et optimisation du calorimètre SuperNEMO et impact sur la recherche de la décroissance du 82Se : Développement du premier prototype LiquidO
Dr Axel Pin
University of Bordeaux / CENBG, 2020, supervised by Christine Marquet and Emmanuel Chauveau
Construction and commissioning of the tracker for the SuperNEMO Demonstrator Module and unfolding the 2vbb spectrum of Mo-100 from the NEMO-3 experiment.
Dr Ashwin Chopra
UCL, 2019, supervised by David Waters
SuperNEMO Experiment: Study of Systematic Uncertainties of Track Reconstruction and Energy Calibration. Evaluation of Sensitivity to 0νββ with Emission of Majoron for 82Se
Dr Miroslav Macko
Comenius University in Bratislava / University of Bordeaux, 2019, supervised by Fabrice Piquemal and Ivan Štekl
Expérience SuperNEMO pour la recherche de la double désintégration bêta sans émission de neutrinos: conception et réalisation du système de déclenchement du module démonstrateur.
Dr Guillaume Oliviero
University of Caen / LPCC, 2018, supervised by François Mauger
Background studies and design optimisation of the SuperNEMO demonstrator module : search for 2νββ and 0νββ decays of 116Cd into the excited states of 116Sn with NEMO-3
Dr Thibaut Le Noblet
Université Grenoble-Alpes / LAPP, 2017, supervised by Dominique Duchesneau and Alberto Remoto
Low background techniques for the SuperNEMO experiment
Dr Xin Ran Liu
UCL, 2017, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Development of reconstruction tools and sensitivity of the SuperNEMO demonstrator
Dr Steven Calvez
Université Paris-Saclay / l'Université Paris-Sud / LAL, 2017, supervised by Laurent Simard and Xavier Garrido
Recherche de la nature du neutrino avec le détecteur SuperNEMO : Simulations optiques pour l'optimisation du calorimètre et performances attendues pour le 82Se
Dr Arnaud Huber
University of Bordeaux / CENBG, 2017, supervised by Fabrice Piquemal and Christine Marquet
The Search for Periodic Modulations of Nuclear Decay Rates with the NEMO-3 Experiment and Development of the Light Injection Monitoring System for the SuperNEMO Experiment
Dr John Cesar
University of Texas at Austin, 2016, supervised by Karol Lang
Search for double beta decay with and without emission of neutrinos of Se-82 to the excited states of Kr-82 in the NEMO3 experiment. Development of apparatuses for ultra-sensitive measurement of Radon emanation for the SuperNEMO experiment
Dr Benjamin Soulé
University of Bordeaux / CENBG, 2016, supervised by Fabrice Piquemal and Frédéric Perrot
Search for double-beta decay of Nd-150 with the NEMO-3 detector
Dr Summer Blot
University of Manchester, 2015, supervised by Stefan Söldner-Rembold
Search for double-beta decay of 96Zr with the NEMO-3 detector and ultra-low radioactivity measurements for the SuperNEMO experiment with the BiPo-3 detector
Dr Guillaume Eurin
UCL / LAL, 2015, supervised by David Waters / Mathieu Bongrand
Search for Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay of Cd-116 and Se-82 and Calorimeter Simulations for the SuperNEMO Experiment
Dr Zachary Liptak
University of Texas at Austin, 2014, supervised by Karol Lang
Search for double-beta decay of 48Ca in NEMO-3 and commissioning of the tracker for the SuperNEMO experiment
Dr Cristóvão Vilela
UCL, 2014, supervised by David Waters
Analyse des données de l’expérience NEMO3 pour la recherche de la désintégration double bêta sans émission de neutrinos. Étude des biais systématiques du calorimètre et développements d’outils d’analyse
Dr Christophe Hugon
University of Bordeaux / CENBG, 2013, supervised by Fabrice Piquemal
Double beta decay of 48Ca with NEMO3 and calibration development for SuperNEMO
Dr Ben Richards
UCL, 2013, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Optimisation du blindage contre les neutrons pour le démonstrateur de SuperNEMO et analyse de la double désintégration β du néodyme-150 vers les états excités du samarium-150 avec le détecteur NEMO 3 (Optimisation of neutron shielding for the SuperNEMO Demonstrator, and analysis of the double-beta decay of Nd-150 to excited states of Sa-150 with the NEMO-3 detector)
Dr Sophie Blondell
Université Paris-Sud / LAL, 2013, supervised by Laurent Simard
Search for double beta decay of 82Se with the NEMO-3 detector and development of apparatus for low-level radon measurements for the SuperNEMO experiment
Dr James Mott
UCL, 2013, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Mesure des processus de double désintégration bêta du Mo-100 versl'état excité 0+1 du Ru-100 dans l'expérience Nemo3. Programme de R&D SuperNEMO : mise au point d'un détecteur BiPo pour la mesure de très faibles contaminations de feuilles sources
Dr Arnaud Chapon
Université de Caen Basse-Normandie / LPCC, 2011, supervised by François Mauger
Development of a tracking software for the SuperNEMO experiment and measurement of Mo-100 half-life with the NEMO 3 experiment
Dr Federico Nova
Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona / IFAE, 2011, supervised by Federico Sánchez Nieto
Search for the neutrinoless double beta decay of 100Mo with the NEMO3 detector and calorimeter research and development for the SuperNEMO experiment
Dr Anastasia Basharina-Freshville
UCL, 2011, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Etude du radon et du thoron par collection électrostatique et par spectrométrie gamma dans le cadre de l'expérience NEMO de décroissance double bêta
Dr Thi Cam Ha Nguyen
CENBG, 2010, supervised by Philippe Hubert and Pham Quoc Hung
Search for Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay of Cd-116 with the NEMO-3 Experiment
Dr Raymond Pahlka
University of Texas at Austin, 2010, supervised by Karol Lang
Double Beta Decay of Nd-150 in NEMO-3 and Studies Towards the Design of SuperNEMO
Dr Christopher Jackson
University of Manchester, 2010, supervised by Stefan Söldner-Rembold
Search for the double beta decay of 96Zr with NEMO-3 and calorimeter development for the SuperNEMO experiment
Dr Matthew Kauer
UCL, 2010, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Développement de compteurs à scintillation hautes performances et de très basse radioactivité pour le calorimètre du projet SuperNEMO
Dr Emmanuel Chauveau
University of Bordeaux / CENBG, 2010, supervised by Fabrice Piquemal and Christine Marquet
Measurement of the Double Beta Decay Half-life of Nd-150 and Search for Neutrinoless Decay Modes with the NEMO-3 Detector
Dr Nasim Fatemi-Ghomi
University of Manchester, 2009, supervised by Stefan Söldner-Rembold
Recherche de la violation de conservation du nombre leptonique total par le processus de double désintégration bêta du 82Se et du 150Nd dans l'expérience NEMO3 : Etude du processus Bi-Po de la chaîne du thoron
Dr Yves Lemière
University of Caen / LPCC, 2008, supervised by François Mauger
Mesure des processus de double désintégration bêta du Te-130 dans l'expérience NEMO 3. R&D du projet SuperNEMO : étude d'un détecteur BiPo.
Dr Mathieu Bongrand
Université Paris-Sud / LAL, 2008, supervised by Corinne Augier
Measurement of the Double Beta Decay Half-Life of 100Mo to the 01+ Excited State, and 48Ca to the Ground State in the NEMO 3 Experiment
Dr Shiva King
UCL, 2008, supervised by Ruben Saakyan
Study of processes of double beta decay of Mo-100 in the NEMO3 experiment (in Russian)
Dr Vera Kovalenko
JINR, 2006, supervised by Victor Brudanin






